Messenger RNA (mRNA)- Definition, Structure, Processing, Types, Functions

mRNA is also known as messenger RNA, is a type of RNA molecule that carries the code from the DNA in the nucleus to the site of protein synthesis in the cytoplasm, ribosome.

- mRNA is the version of the genetic materials that leave the nucleus and move to the cytoplasm where responsible proteins are synthesized.
- The information in DNA cannot be translated directly to proteins, it must be transcribed into this RNA form, called mRNA that now encodes for specific proteins.
- This process of transcribing the information in DNA to mRNA is called Transcription, which is catalyzed by the enzyme, RNA polymerase.
- mRNA being an RNA is a single-stranded molecule and the length of ribonucleotides present in mRNA can vary according to the regions of the DNA transcribed considering the type of proteins needed by the cell.
- With each three-nucleotide base sequence in the mRNA molecule, one specific amino acid is coded, and subsequently, a chain of amino acids (proteins) is obtained by decoding these base sequences in the mRNA molecule.
- These codes are in the form of triplet sequences of nitrogenous bases and are often referred to as codons.
Table of Contents
Interesting Science Videos
Messenger RNA (mRNA) Properties
- mRNA accounts for about 5% of the total RNA present in the cell.
- The length of ribonucleotides in an mRNA molecule varies widely, depending on the type of protein they account to code for. Therefore, the mRNA molecule is considered the most heterogeneous of the 3 types of RNA present in the cell.
- mRNA is synthesized from a DNA molecule by the action of enzyme RNA polymerase and the process is termed transcription.
- At the end of transcription, mRNA is synthesized. This newly synthesized mRNA is further edited or modified to remove non-coding regions and also to make the molecule stable, this process is called post-translational modification, and takes place only in the eukaryotic cell.
- During post-transcriptional modification, along with the cleaving out of non-coding regions from mRNA molecule, they are capped on their 5’ end with guanosine triphosphate nucleotide, to make it recognizable to the ribosome during protein synthesis.
- Additionally, during the post-transcriptional modification process, the 3’ end of mRNA molecule is also edited by adding numerous adenines monophosphates at their end, also referred to as Poly A tail, which makes the mRNA molecule more stable by preventing enzymatic degradation.
- mRNAs are sensitive to heat and can be degraded on prolonged exposure to high temperatures. However, for some manipulations, they can be heated for a specific period of time at distinct high temperatures.
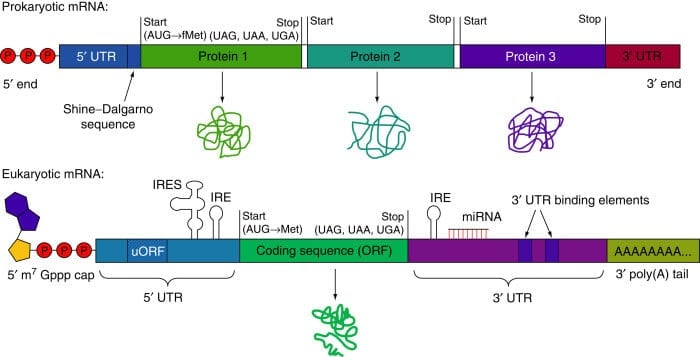
Figure: Structure of Prokaryotic mRNA and Eukaryotic mRNA. Image Source: D.J.Goss and A.V.Domashevskiy.
Structure of mRNA

- mRNA is a single-stranded RNA molecule running from 5’ to 3’ direction.
- In a prokaryotic cell, there is a lack of a distinct nucleus, thus the mRNA synthesized contained a copy of DNA sequences with a terminal 5’- triphosphate group and 3’ hydroxyl group. Prokaryotic mRNA at its 5’ end has a Shine Dalgarno sequence which is rich in purine nucleotide and is essential for facilitating the binding of mRNA to ribosome.
- Prokaryotic mRNA starts at 5’ with a triphosphate group, followed by Shine Dalgarno sequences (untranslated region) and as we move along to the 3’ direction, the coding regions begin. The coding regions begin with a start codon and end when it reaches a stop codon, after encountering a stop codon, protein-coding regions come to an end, after which there is another untranslated region that terminates at the end of 3’.
- However, in a eukaryotic cell, the nucleus is distinct and has numerous enzymes in it that make the synthesized mRNA molecule go through modification at their terminals 5’ and 3’ to maintain the integrity and stability of the mRNA molecule (post-transcriptional modification).
- The 5’ triphosphate group of eukaryotic mRNAs is esterified forming a cap structure. This process is referred to as 5’ capping, which happens when a 7-methylguanosine cap is added to a 5’ free triphosphate group via 5’-5’ phosphate linkage with the help of an enzyme called guanyl transferase.
- The 5’ capping is important for the recognition of mRNA by the Ribosomes during protein synthesis.
- And likewise, the 3’ hydroxyl group is cleaved to give a free hydroxyl group to which numerous adenine monophosphates are added to make the mRNA molecule more stable and prevent it from degradation. This tail of numerous adenine nucleotides is referred to as Poly-A-tail.
- The Poly-A-tail added to the 3’ end of eukaryotic mRNA are usually 100-200 bases long; the addition is catalyzed by an enzyme poly(A) polymerase that recognizes the sequence AAUAAA as a single for addition.
- The poly-A-tail is vital during transporting mRNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm for proteins synthesis.
- Eukaryotic mRNA starts at 5’ with a cap followed by untranslated regions (5’ UTR), and as we move along 3’ direction, the coding regions begin with the start codon and continue till it reaches the stop codon, which marks the termination of coding regions, after which there is another untranslated region (3’ UTR) that terminate when Poly-A-tail begins, which further terminates at the end of 3’.
Figure: Eukaryotic mRNA Structure. Image Source: TransControl.
Messenger RNA (mRNA) Composition
- mRNA is a biopolymer of nucleotides bonded with each other via a phosphodiester bond.
- The number of nucleotides in mRNA varies widely according to the type of proteins it can encode.
- The nucleotide that makes up the mRNA are also referred to as Ribose nucleotide due to the presence of ribose sugar in their structure. Overall, mRNA is composed of a ribose sugar, phosphate, and nitrogenous base.
- Ribose sugar is a cyclical structure made up of five carbons and one oxygen atom. This sugar contains two OH-groups at 2’ Carbon and 3’ Carbon.
- This ribose sugar is attached to a nitrogenous base via a glycosidic bond.
- There are four nitrogenous bases namely: Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Uracil (U), and Cytosine (C).
- These nitrogenous bases pair complementarily with each other: G with C and A with U.
- A mature mRNA in the eukaryotic cell also consists of a modified 5’ end with a 7-methylguanosine cap on it and a modified 3’ end with poly adenine nucleotides on it.
- Eukaryotic mRNA before post-transcriptional modification is called precursor mRNA having both non-coding regions(introns) and coding regions (exons) and no 5’ cap and 3’ poly-A-tail on it.
- But after post-transcriptional modification of precursor mRNA of the eukaryotic cell, the non-coding regions are cleaved out, and 5’ capping and 3’ poly-A-tail are present on mRNA thus making it a mature mRNA ready for protein synthesis.
- However, in a prokaryotic cell, no such post-translational modification takes place, so the mRNA synthesized has both coding and non-coding regions on them, additionally, no capping and poly-A-tail are observed, making them prone to degradation.
- We now can say that the composition of mRNA depends on the type of cell they are in, and in what phase of their processing they are in.
Messenger RNA (mRNA) Processing
mRNA processing refers to the steps that are carried out before mRNA is finally ready for protein synthesis. When mRNA is synthesized from the DNA molecule, the mRNA we will get is a precursor mRNA having the same 5’ triphosphate and 3’ hydroxyl terminal residues as that of the DNA. This newly transcribed pre- mRNA is prone to degradation so to protect it, this pre-mRNA is coated with RNA stabilizing proteins as soon as they are synthesized. Not only that, but the stabilizing proteins are also responsible for the safe deliver of mRNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm.
This precursor mRNA processing happens in three important steps:
1. Addition of stabilizing and signaling factors at 5’ end. (5’ capping)
- When pre-mRNA is being synthesized, its 5’ end is immediately capped by a 7-methylguanosine cap via 5’-5’ phosphate linkage.
- This cap structure protects the mRNA from degradation and in addition. They also help in the recognition of the mRNA molecule by initiation factors involved in protein synthesis to initiate translation in Ribosome.
2. Addition of stabilizing and signaling factors at 3’ end. (Poly-A-tail)
- The newly synthesized mRNA from double-stranded DNA with the activity of an enzyme, RNA polymerase, is premature to initiate protein translation so to make it mature.
- In addition to 5’ capping, 3’ end of pre-mRNA also needs some modifications and this is carried out by an enzyme that cleaves the 3’ end and adds numerous adenine nucleotides to it. Thus, making a poly-A-tail at the 3’ end of pre-mRNA. The number of adenine nucleotides added is said to be about 200 approx.
- This poly-A-tail prevents mRNA from degrading and plays a vital role in transporting mature mRNA from the nucleus into the cytoplasm for protein synthesis.
3. Precursor mRNA splicing
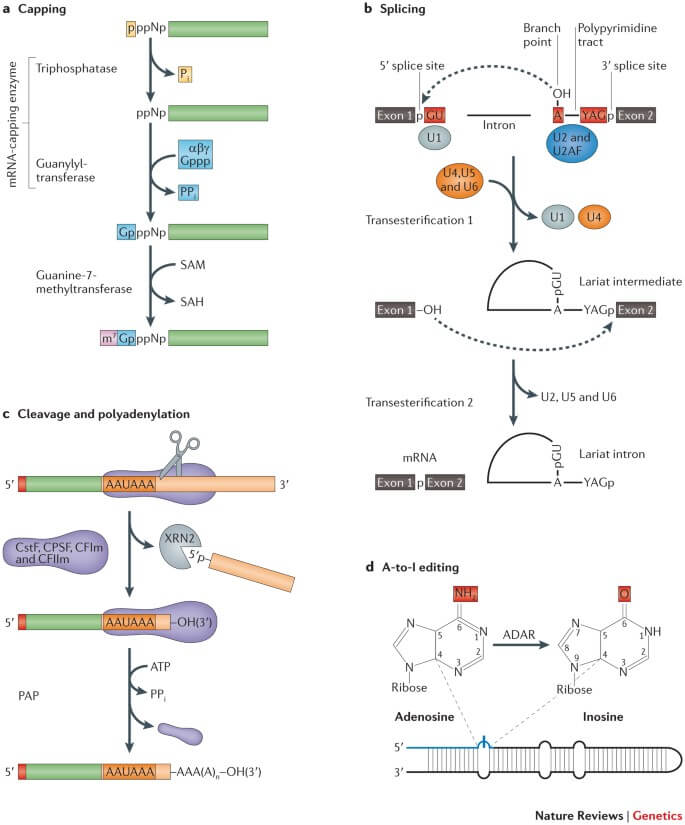
- Genetic information transcribed from DNA molecules contains both introns and exons, but for mRNA to be translation-ready it must only have exons, so we have to splice these introns out and keep only exons. This process of removing introns and keeping only exons in the mRNA sequence is called mRNA splicing.
- The process of splicing occurs by recognizing a specific sequence that initiates the cleaving out of the introns and rejoining of exons with utmost precision and accuracy. The splicing process is made possible by complexes of proteins and RNA molecules called Spliceosomes.
- Each of these spliceosomes consists of five subunits called snRNPs (for small nuclear ribonucleoproteins) . These snRNPs are only found in the nucleus.
- These spliceosomes recognize sequences at the 5′ end and 3’ end of the intron, the specific sequences they recognize are GU nucleotide at the start of 5’ end and AG nucleotide at the end of 3’ end.
- Now that these spliceosomes recognize the introns, they cleave them out by breaking the sugar-phosphate of pre-mRNA at the 5’ end of introns and covalently attaching it to A nucleotide internally within the intron. This results in cleaving out of introns.
- Spliceosomes now connect the free 3’ end of one exon to the adjoining exon with a free 5’ end, thus making the joining possible. Now, the mRNA that we have is a mature mRNA with a 5’ cap, 3’ poly-A-tail, and only exons.
Figure: The major co-transcriptional mRNA processing steps. Image Source: Nature Reviews Genetics.
Types of mRNA
1. Precursor mRNA
- It is a primary transcript for a mature mRNA as it comes off the DNA template.
- The pre-mRNA contains sequences that are removed before translation.
- These sequences are removed by the action of complexes of protein and RNA molecules called Spliceosomes.
- In addition to the removal of sequences, some modifications are carried out at 5’ and 3’ ends respectively.
- After all, the unwanted sequences are removed and the 5’ and 3’ ends are modified it is ready for translation, now we term it as mature mRNA.
2. Monocistronic mRNA
- This type of mRNA molecule contains exons regions that code for a single protein.
- All eukaryotic mRNA is monocistronic, and they all go through post-translational modification to initiate protein synthesis.
- It is transcribed from a single gene (cistron) and has one initiation and termination codon.
3. Polycistronic mRNA
- In contrast to monocistronic mRNA, this molecule of mRNA encodes for more than one protein.
- Present in a prokaryotic cell, and also in the chloroplast of plants.
- It is transcribed from more than one gene and thus has many initiations and terminations codons.
Functions of Messenger RNA (mRNA)
- The primary function of mRNA is to transcribe the information present in a DNA strand into an essential protein, that is required for the cell.
- The central dogma is the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA and then to protein. Since DNA cannot be directly coded to proteins, mRNA acts as an intermediary between DNA and proteins.
- mRNA-based therapeutics are emerging as a promising class of therapeutic drugs. Just recently some COVID vaccines are using this mRNA technology to induce an immune response in the patients rather than using the attenuated virus.
- mRNAs have made the formation of a complementary DNA library possible.
- Defects or mutations in DNA can result in faulty transcription of mRNA and eventually a faulty protein that might cause complications.
References
- Bentley, D. Coupling mRNA processing with transcription in time and space. Nat Rev Genet15, 163–175 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3662.
- Van Lint S, Heirman C, Thielemans K, Breckpot K. mRNA: From a chemical blueprint for protein production to an off-the-shelf therapeutic. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2013;9(2):265-274. doi:10.4161/hv.22661.
- Wang D, Farhana A. Biochemistry, RNA Structure. [Updated 2021 May 9]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK558999/.
- Shyu AB, Wilkinson MF, van Hoof A. Messenger RNA regulation: to translate or to degrade. EMBO J. 2008;27(3):471-481. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7601977.
- Cooper GM. The Cell: A Molecular Approach. 2nd edition. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates; 2000. Translation of mRNA. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK9849/.
- https://www.britannica.com/science/nucleic-acid/Methylation#ref594024
- https://www.genome.gov/genetics-glossary/messenger-rna
- https://www.modernatx.com/mrna-technology/science-and-fundamentals-mrna-technology
- https://www.cd-genomics.com/blog/mrna-fact-sheet-definition-structure-function-and-association-with-disease/
- https://www.sparknotes.com/biology/molecular/posttranscription/section1/
- https://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-biology/chapter/rna-processing-in-eukaryotes/
- https://biologydictionary.net/mrna/
- https://www.ndsu.edu/pubweb/~mcclean/plsc731/transcript/transcript3.htm
- https://www.majordifferences.com/2013/05/difference-between-polycistronic-and.html
About Author
Rajat Thapa did his undergraduate studies (B.Sc.) in Microbiology at St. Xavier's College, Kathmandu, Nepal, and is interested in Public Health. He is currently working as a Junior Embryologist at Angel Fertility Clinic. He has published two research articles and looks forward to doing some work in Antimicrobial resistance. He has invested himself in learning things that can help him to get to the goals he has set for himself.
4 thoughts on “Messenger RNA (mRNA)- Definition, Structure, Processing, Types, Functions”
Authors say: “Each of these spliceosomes consists of five subunits called snRNPs (for small nuclear ribonucleoparticles. ” This is wrong. snRNPs mean small nuclear ribonucleoproteins, not particles. Reply
Sagar Aryal
Thanks for the correction, the error has been corrected 🙂 Reply
Authors say: “This ribose sugar is attached to a nitrogenous base via hydrogen bonding.” This is completely wrong, because ribose bound to the nitrogenous base is definitely covalent. Hydrogen bond is too weak to be implemented in DNA/RNA chain. Reply
Sagar Aryal
Thanks for the correction, the error has been corrected 🙂 Reply
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Topics / Categories

- Agricultural Microbiology (13)
- Bacteriology (124)
- Basic Microbiology (61)
- Biochemical Test (114)
- Biochemistry (165)
- Bioinformatics (23)
- Biology (209)
- Biotechnology (31)
- Cell Biology (107)
- Culture Media (67)
- Difference Between (89)
- Diseases (32)
- Environmental Microbiology (7)
- Epidemiology (23)
- Food Microbiology (51)
- Genetics (79)
- Human Anatomy and Physiology (75)
- Immunology (115)
- Instrumentation (64)
- Microscopy (27)
- Molecular Biology (78)
- Mycology (33)
- Parasitology (26)
- Pharmacology (14)
- Phycology (2)
- Protocols (9)
- Research Methodology (20)
- Staining (29)
- Syllabus (18)
- Virology (50)
- Mycorrhiza: Definition, Types and Significances
- Marine Ecosystem and its Abiotic and Biotic Components
- Homeostasis: Definition, Types, Examples, Applications
- Neutrophils: Definition, Structure, Count, Range, Functions
- Whole Transcriptome Sequencing (WTS) / Total RNA-Seq







